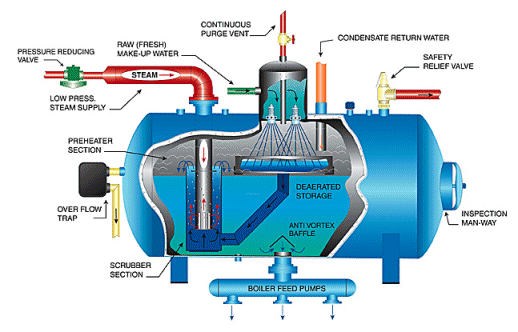
Boiler Water Chemicals
Boiler water treatment chemicals play a crucial role in enhancing boiler efficiency and mitigating issues such as scale accumulation, corrosion, and foaming.
These additives play a crucial role in protecting the metal elements of the boiler and facilitating effective heat transfer. Common varieties consist of oxygen scavengers, alkalinity adjusters, scale and corrosion inhibitors, and amines.

Here's a more detailed look at the different types:

Oxygen Scavengers:
Purpose: Remove oxygen that is dissolved in boiler water to prevent corrosion from occurring.
Frequently Used Chemicals:
- Sulfite base
- Hydrazine base
- DEHA (Diethylhydroxylamine) base

Alkalinity Enhancers:
- Purpose:
Adjust and maintain the pH of boiler water to prevent corrosion and scale formation.
Common Chemicals:
- Sodium hydroxide Base
- Amine Base

Scale Control Agents:
- Objective: To inhibit the accumulation of scale on boiler surfaces through protective coatings, thereby enhancing heat transfer efficiency and reducing the risk of overheating.
- Widely Used Chemicals:
ZEELCHEM Phosphates and ZEELCHEM Polymers.

Corrosion Inhibitors:
Unleashing power with elegance, the Koran Mini blends advanced engineering with classic design, delivering a thrilling ride that’s both swift and smooth.

Amines Compounds:
Aim: Counteract acidic condensate and avert corrosion in condensate pipelines.
Standard Chemicals: Morpholine

Other Compounds:
- Sludge Treatment Agents/Sludge Conditioner
Contribute to the reduction of sludge formation and keep it evenly distributed, which enhances heat transfer.
- Coagulants/Coagulating substances Facilitate the removal of suspended solids from boiler water.
- Defoaming agents/Defoamer
Minimize foaming to prevent the migration of solids into the steam.
Crucial Aspects:
- Type of Boiler:
Different boiler systems, such as steam and hot water, might need specific chemical treatments tailored to their requirements. - Operating Pressure Level:
The pressure levels in a boiler impact the choice of chemicals and the treatment strategies applied. - Quality of Feedwater:
The properties of the feedwater, including hardness and dissolved solids, significantly affect the chemical treatment approach. - Consistent Evaluation:
Consistently analyzing boiler water and condensate is essential for tracking water chemistry and ensuring effective treatment. - Professional Advice:
It is advisable to consult a water treatment expert to identify the most suitable chemical treatment strategy for your particular boiler system.